Introduction: Understanding VPN Security and Vulnerabilities
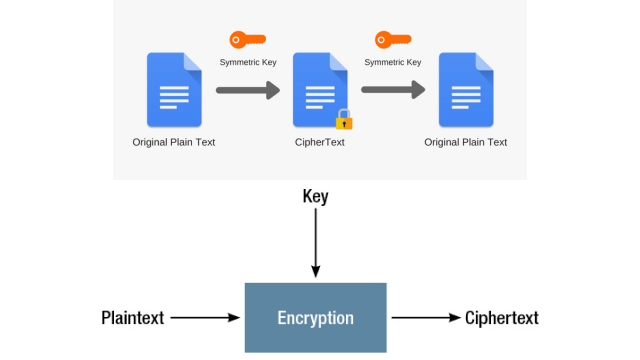
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are a popular tool for users who want to keep their internet activities private and secure. By creating an encrypted tunnel between a user’s device and a remote server, a VPN allows users to hide their IP address and encrypt their internet traffic, making it difficult for others to intercept or monitor their online activities.
However, despite the benefits of VPNs, there are still some security vulnerabilities that users should be aware of. One common vulnerability is a DNS leak, where a user’s DNS requests are not routed through the VPN, exposing their true IP address to third parties. Another vulnerability is a WebRTC leak, where a user’s real IP address can be revealed by certain web browsers even when they are using a VPN.
In addition to these vulnerabilities, there are also other potential risks to using a VPN, including the possibility of connection logs being stored by the VPN provider, which could potentially be used to identify a user’s online activities. There is also the risk of VPN providers being hacked themselves, potentially exposing users’ sensitive data.
To stay safe while using a VPN, users should choose a reputable provider that does not store connection logs, use a VPN kill switch to ensure that their internet traffic is always routed through the VPN, and regularly check for DNS and WebRTC leaks. By understanding the potential vulnerabilities and taking appropriate measures to protect themselves, users can enjoy the benefits of using a VPN without compromising their online security.
Vulnerability #1: Outdated Protocols and Encryption Standards
One of the most common vulnerabilities that VPNs face is the use of outdated protocols and encryption standards. VPN protocols are used to establish a secure and encrypted connection between the user’s device and the VPN server. However, some of these protocols and encryption standards are no longer considered secure due to advancements in technology and hacking techniques.
For example, the outdated Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is vulnerable to hacking attacks and should be avoided. Similarly, the use of outdated encryption standards, such as DES or RC4, can leave a VPN connection vulnerable to attacks.
To stay safe, it’s essential to use VPNs that support modern protocols and encryption standards, such as OpenVPN, IKEv2, or WireGuard. When choosing a VPN provider, always check their website to ensure that they use up-to-date protocols and encryption standards. Additionally, it’s crucial to keep your VPN client and operating system updated to ensure that any security vulnerabilities are patched promptly.
Vulnerability #2: DNS Leaks and IP Address Exposures
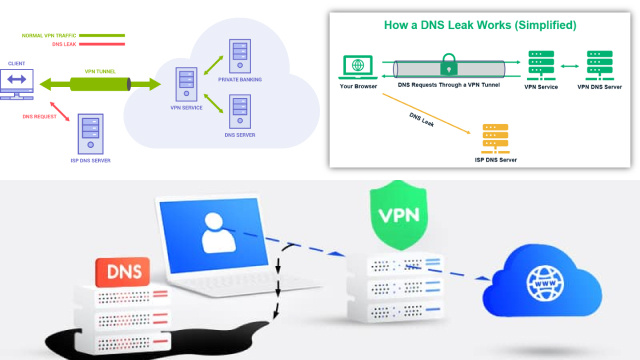
One of the vulnerabilities that can compromise the security of a VPN is DNS leaks and IP address exposures. When using a VPN, your device should be connected to a server that masks your real IP address and encrypts all your internet traffic. However, if the VPN service does not have adequate measures to prevent DNS leaks or IP address exposures, your online activity can be traced back to your real IP address.
A DNS leak occurs when your device sends DNS queries outside the VPN tunnel, revealing your true location and IP address. This can happen if the VPN’s DNS servers are not properly configured or if your device is configured to use other DNS servers. Additionally, some VPN services may not have adequate measures in place to prevent IP address exposures, which can happen if their servers are compromised or if there are flaws in their software. To avoid these vulnerabilities, it is important to choose a VPN service that has strong encryption, DNS leak protection, and a solid track record for protecting user privacy.
Vulnerability #3: Malware Attacks and VPN Exploits
Another vulnerability that users need to be aware of is the possibility of malware attacks and VPN exploits. Malware can infiltrate a user’s device through a variety of methods, such as phishing emails or infected downloads. Once the malware is on the device, it can bypass the VPN connection and access sensitive data. Additionally, hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the VPN software itself to gain access to the user’s network.
To mitigate the risk of malware attacks and VPN exploits, it’s important to keep your device’s security software up-to-date and to be cautious when downloading files or clicking links. Users should also research VPN providers to ensure that they use strong encryption and have a track record of protecting against these types of attacks. By taking these steps, users can help protect themselves from the risk of malware and VPN exploits.
Vulnerability #4: Public Wi-Fi Risks and Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
When you connect to public Wi-Fi without a VPN, your data is vulnerable to interception by hackers using man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks. These attacks involve intercepting and modifying data in transit between your device and the Wi-Fi router. This can allow attackers to steal sensitive information such as login credentials or financial information. Even if the public Wi-Fi is password-protected, it’s not enough to keep your data safe.
Using a VPN can help mitigate this risk by encrypting your internet traffic and making it much more difficult for hackers to intercept and read your data. However, not all VPNs are created equal, and some may not offer adequate protection against MitM attacks. It’s important to choose a VPN provider with strong encryption and security features to ensure your data is fully protected while using public Wi-Fi networks.
Vulnerability #5: VPN Logging and Data Retention Policies
One of the biggest concerns with VPN usage is the logging and retention of user data. While VPN providers claim to have a no-logging policy, it’s important to read the fine print and understand what they do with your information. Some VPNs may collect data on your browsing activity, IP address, and even keep records of your connection times. This information could be used against you in the event of a data breach or government subpoena.
Additionally, some VPNs may be required to retain user data for a certain period of time due to local laws or regulations. This means that even if a VPN claims to have a no-logging policy, they may still be collecting and storing your data. To stay safe, it’s important to thoroughly research a VPN’s logging and data retention policies before choosing to use their service.
How to Stay Safe: Best Practices for Using a VPN
Using a VPN can greatly enhance your online privacy and security, but it’s important to keep in mind that no security measure is foolproof. To reduce the risks of vulnerabilities in VPNs, there are a few best practices you should follow.
First, always use the latest version of your VPN software and keep it up-to-date. This ensures that any security flaws or bugs are patched. Additionally, make sure to use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication whenever possible to prevent unauthorized access.
It’s also important to choose a reputable VPN provider that has a strict no-logging policy and transparent data retention practices. You should also avoid using free VPN services as they may not be trustworthy and may even sell your data.
Another best practice is to avoid using public Wi-Fi networks, as they are often not secure and can be easily compromised by hackers. Instead, use your VPN on a trusted network or create a secure hotspot with your mobile device.
Lastly, be mindful of the websites you visit and the information you share online. While a VPN can protect your data from eavesdropping, it can’t prevent you from falling victim to phishing scams or social engineering attacks.
VPN Alternatives: Exploring Other Privacy-Enhancing Tools
While Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are highly effective tools for safeguarding online privacy, they are not the only options available. Various privacy-enhancing tools and techniques can provide online security and protect your data. Here are some notable VPN alternatives:
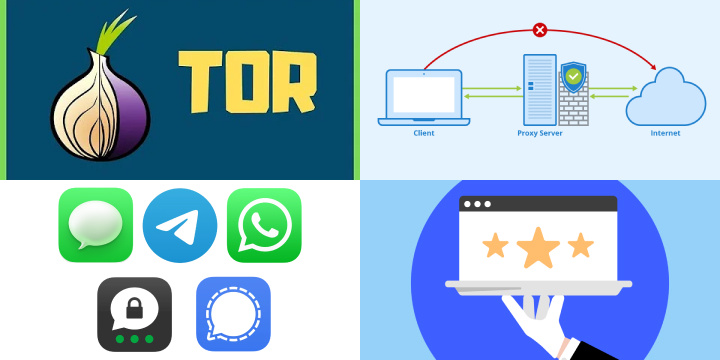
- Tor (The Onion Router): Tor is a network that routes your internet traffic through a series of volunteer-operated servers, making it challenging to trace your online activities. It is particularly effective for anonymous browsing.
- Proxy Servers: Proxy servers act as intermediaries between your device and the internet. They can hide your IP address and offer a level of anonymity, although they may not provide the same level of security as VPNs.
- Encrypted Messaging Apps: Secure messaging apps like Signal and Telegram offer end-to-end encryption, ensuring your messages remain private and protected from interception.
- Privacy-Focused Browsers: Browsers like Mozilla Firefox with privacy-focused extensions and configurations can enhance your online privacy by blocking trackers and ads.
- Secure Email Services: Services like ProtonMail and Tutanota provide encrypted email communication, ensuring that your email content remains confidential.
- Virtual Machines (VMs): Using VMs can provide an extra layer of security by isolating your online activities in a virtual environment, reducing the risk of malware affecting your main system.
- DNS Encryption: Employing encrypted DNS services like DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) or DNS-over-TLS (DoT) can protect your browsing privacy by securing the process of translating domain names to IP addresses.
- Browser-Based Privacy Tools: Browser extensions like Privacy Badger, uBlock Origin, and HTTPS Everywhere can help block trackers and enhance your online privacy.
- Proactive Security Practices: Regularly updating software, using strong, unique passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and staying vigilant against phishing attacks are fundamental to online security.
- Secure Cloud Services: Utilizing encrypted cloud storage and file-sharing services like Sync.com and pCloud can protect your data from unauthorized access.
Selecting the right privacy-enhancing tool depends on your specific needs and the level of privacy you require. It’s essential to evaluate the trustworthiness and security features of any tool or service you choose and consider combining multiple methods to create a robust privacy strategy. Whichever method you opt for, prioritizing online privacy is crucial in the digital age.
Conclusion: The Importance of Protecting Your Online Privacy and Security
In conclusion, protecting your online privacy and security is of paramount importance in today’s digital age. VPNs are a valuable tool for safeguarding your internet connection and keeping your data private. However, as with any technology, there are vulnerabilities and risks associated with using a VPN. By understanding these vulnerabilities and following best practices for using a VPN, you can minimize the risks and enjoy a more secure online experience.
To stay safe while using a VPN, make sure to use updated encryption protocols and avoid free VPN services that may compromise your privacy. Additionally, be aware of potential DNS leaks and IP address exposures, and always connect to trusted networks to avoid public Wi-Fi risks and man-in-the-middle attacks. Finally, choose a VPN provider with a strict no-logging policy and data retention policy.
By taking these precautions and staying informed about the latest developments in VPN security, you can rest assured that your online activities are protected and your personal information remains private.