Introduction
In today’s digital age, online privacy and security have become increasingly important concerns. As a result, many people have turned to tools like DNS and VPN to protect their online activities from prying eyes. While these two technologies may seem similar, they serve different functions and offer different levels of protection.
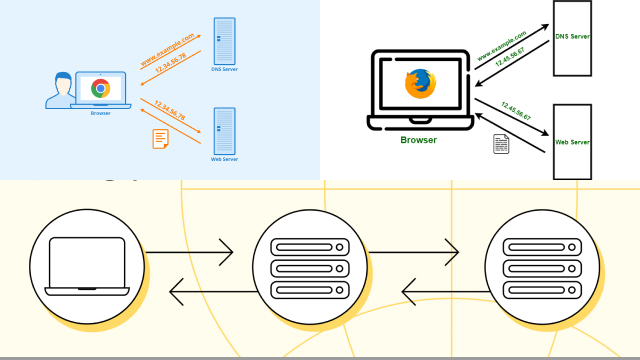
DNS (Domain Name System) is a fundamental part of the internet infrastructure that translates domain names into IP addresses. Every time you access a website or an online service, your device sends a DNS request to a DNS server to resolve the domain name into an IP address.
On the other hand, a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a tool that encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a private network of servers operated by a VPN provider. This means that your online activities are hidden from your internet service provider and other potential snoopers.
Understanding the difference between DNS and VPN is essential to choosing the right tool to protect your online activities. In this article, we will explore the key differences between DNS and VPN, and discuss the pros and cons of using each technology.
What is DNS?
DNS (Domain Name System) is a critical part of the internet infrastructure that translates domain names into IP addresses. When you enter a URL into your web browser, your device sends a DNS request to a DNS server to resolve the domain name into an IP address. This is necessary because computers communicate using IP addresses, but humans find it easier to remember domain names.
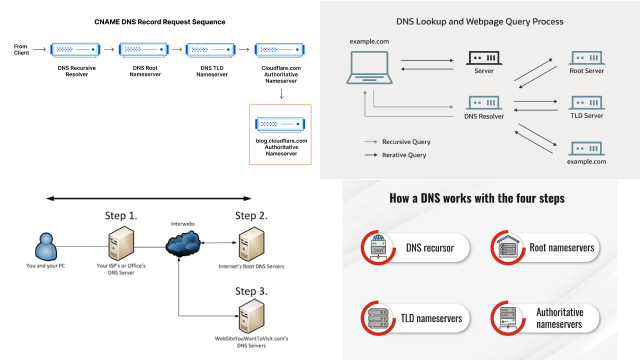
DNS works by using a hierarchical system of servers that are responsible for storing and distributing information about domain names and their associated IP addresses. At the top of this hierarchy are the root servers, which store information about top-level domains like .com, .org, and .net. Below the root servers are the top-level domain (TLD) servers, which store information about the specific TLDs, such as .com or .org. Finally, there are the authoritative name servers, which store information about individual domain names.
By translating domain names into IP addresses, DNS allows devices to communicate with each other over the internet. However, DNS can also be a potential security risk, as hackers can intercept DNS requests and redirect users to fake websites. This is known as a DNS hijacking attack and can be used to steal sensitive information like passwords and financial data.
How DNS works
DNS works by using a hierarchical system of servers that store and distribute information about domain names and their associated IP addresses. When you enter a URL into your web browser, your device sends a DNS request to a DNS server to resolve the domain name into an IP address. The DNS server then queries other servers in the hierarchy until it finds the authoritative name server that holds the IP address for the requested domain name. Once the IP address is retrieved, the DNS server returns it to your device, allowing it to connect to the requested website or service. DNS also uses caching to speed up the process by storing recently accessed IP addresses for a certain period of time, reducing the need for repeated queries.
What is a VPN?
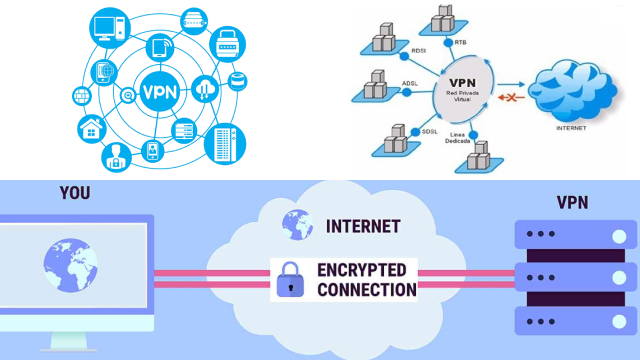
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a tool that encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a private network of servers operated by a VPN provider. This means that your online activities are hidden from your internet service provider and other potential snoopers. When you connect to a VPN, your device creates a secure and encrypted tunnel between itself and the VPN server.
All of your internet traffic passes through this tunnel, making it invisible to anyone outside the VPN network. This provides a level of privacy and security that is not possible when using a regular internet connection. VPNs are commonly used by individuals and organizations to protect their online activities, bypass internet censorship, and access restricted content.
How VPN works
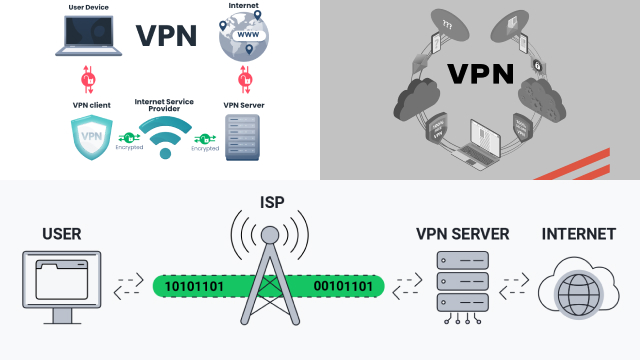
A VPN works by creating a secure and encrypted connection between your device and a VPN server. When you connect to a VPN, your internet traffic is encrypted and routed through the VPN server before it reaches its final destination. This means that anyone trying to intercept your online activities will only see encrypted traffic, making it virtually impossible to decipher the data being transmitted.
The VPN server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet, allowing you to access the internet as if you were in a different location. For example, if you connect to a VPN server located in the United States, your device will appear as if it is located in the United States, even if you are physically located in a different country.
VPNs use different protocols to establish the secure connection between your device and the VPN server, IKEv2, and L2TP/IPsec. These protocols help to ensure that your data is encrypted and transmitted securely over the internet.
Overall, a VPN provides a level of privacy and security that is not available with a regular internet connection. By encrypting your online traffic and hiding your IP address, a VPN helps to protect your online activities from prying eyes, making it a valuable tool for anyone concerned about online privacy and security.
DNS vs. VPN: Key Differences
DNS and VPN are two different tools that serve different purposes in protecting online privacy and security. DNS (Domain Name System) is a protocol used to translate domain names into IP addresses, while a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a tool that encrypts and routes internet traffic through a private network of servers.
The key difference between DNS and VPN is that DNS does not encrypt internet traffic or hide IP addresses, while a VPN provides both of these features. DNS simply translates domain names into IP addresses, allowing your device to connect to the requested website or service. However, this process can be intercepted by third parties, such as your internet service provider, potentially allowing them to see your online activities.
On the other hand, a VPN encrypts all internet traffic and routes it through a private network of servers, making it virtually impossible for anyone outside the VPN network to see your online activities. Additionally, a VPN also allows you to hide your IP address and appear as if you are accessing the internet from a different location, providing an extra layer of privacy and security.
Which one should you use?
The decision to use DNS or VPN ultimately depends on what you are looking to achieve. If your primary concern is accessing websites or services that may be blocked in your location, then DNS may be a suitable option for you. DNS allows you to bypass geographical restrictions and access content that may not be available in your country.
However, if you are concerned about online privacy and security, then a VPN is the better choice. A VPN provides a secure and encrypted connection that protects your online activities from being intercepted by third parties, such as your internet service provider or government agencies. A VPN also allows you to browse the internet anonymously by hiding your IP address and location.
Furthermore, a VPN is also useful when using public Wi-Fi networks, as it protects your online activities from potential hackers who may be lurking on the same network.
In conclusion, while DNS and VPN serve different purposes, a VPN is the recommended option for those who are concerned about online privacy and security. However, if your only concern is accessing blocked content, then DNS may be a viable option for you.
Using DNS and VPN together: Pros and Cons
Using DNS and VPN together can provide additional security and privacy benefits, but it also has its pros and cons.
One advantage of using DNS and VPN together is that it can help prevent DNS leaks. DNS leaks can occur when using a VPN, and they happen when your device uses its default DNS server instead of the encrypted DNS server provided by the VPN. By using a secure DNS server alongside a VPN, you can ensure that your online activities remain private and protected.
Another advantage is that using DNS and VPN together can provide faster internet speeds. DNS servers can help optimize your internet connection, while VPNs can slow down your connection due to encryption and server distance. By using a DNS server to optimize your connection, you can improve your internet speed while still benefiting from the added security of a VPN.
On the other hand, using DNS and VPN together can also have its downsides. Using multiple security services can lead to compatibility issues and cause technical problems. Furthermore, it can also be more expensive to use both services together, as you may need to pay for separate subscriptions.
In conclusion, using DNS and VPN together can provide additional security and privacy benefits, but it also has its drawbacks. It’s important to weigh the pros and cons and assess whether using both services together is necessary for your online security and privacy needs.
Maximizing Online Privacy: Combining DNS and VPN for Enhanced Security
In the digital age, privacy and security concerns are paramount. Two fundamental tools that individuals and organizations employ to safeguard their online activities are DNS (Domain Name System) and VPN (Virtual Private Network). Combining these technologies can provide a robust defense against potential threats and enhance online privacy significantly.
DNS (Domain Name System) acts as the internet’s phone book, translating human-friendly domain names into IP addresses for website routing. While DNS services provided by your ISP (Internet Service Provider) are common, alternative DNS services like OpenDNS and Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1 offer improved security features, such as malware filtering and enhanced privacy.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) creates a secure, encrypted tunnel for data transmission between your device and a VPN server. This shields your internet traffic from prying eyes, making it an effective tool for maintaining anonymity and protecting data on public Wi-Fi networks.
When combined, DNS and VPN provide a layered approach to online privacy:
- Enhanced Privacy: DNS-over-VPN routes DNS queries through the encrypted VPN tunnel, preventing ISPs from monitoring your browsing habits.
- Geographic Bypass: VPNs can help bypass geographic restrictions, while DNS services can optimize access and provide faster browsing speeds.
- Malware and Phishing Protection: DNS services can block malicious domains, adding an extra layer of security when used with a VPN.
- Customization: Users can choose specific DNS and VPN services that align with their privacy and security preferences.
However, it’s important to select reputable DNS and VPN providers, as the effectiveness of these services depends on their trustworthiness. Additionally, users should consider potential trade-offs in terms of connection speed, as VPNs may introduce some latency.
In conclusion, combining DNS and VPN technologies can create a robust shield against online threats, enhance privacy, and provide greater control over your internet experience. Careful selection and configuration of these services can maximize the protection of your online activities, helping you maintain a safer and more private digital presence.