Introduction to Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security process that requires users to provide two forms of identification before gaining access to an account or system. The first factor is usually a password or PIN, and the second factor can be a fingerprint, face recognition, code sent via text or email, or a physical device such as a security key.
2FA provides an additional layer of security to protect against unauthorized access, especially in cases where passwords are compromised. It is becoming increasingly popular, and many websites and services now offer this option as an added security feature.
While 2FA is not foolproof, it significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and helps safeguard personal and sensitive information. It is important to note that enabling 2FA does not mean that an account is completely secure, and users should still take precautions such as regularly changing passwords and keeping their devices and software up-to-date.
Overall, implementing 2FA is a simple yet effective way to enhance the security of personal and business accounts and minimize the risk of data breaches and identity theft.
What Is the Purpose of Two-Factor Authentication?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is an additional layer of security that helps protect your online accounts from unauthorized access. With 2FA, you need to provide two different types of authentication to access your account, such as a password and a unique code sent to your phone or generated by an authentication app.
The purpose of 2FA is to make it more difficult for hackers and cybercriminals to gain access to your online accounts, even if they have obtained your password through a data breach or other means.
By requiring a second form of authentication, 2FA adds an extra level of security to your accounts and makes it more difficult for someone to impersonate you and access your personal information.
While 2FA is not foolproof and does not guarantee complete security, it is an effective way to improve the security of your online accounts and protect your personal information from unauthorized access.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication Methods
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring two forms of authentication to log in. There are several types of 2FA methods available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common method is SMS-based 2FA, where a one-time code is sent to your phone via text message. Another popular method is a mobile authentication app, such as Google Authenticator or Authy, which generates a code that changes every 30 seconds.
A physical security key, such as YubiKey or Titan Security Key, is also a reliable option that plugs into your computer or device and provides a unique code when pressed.
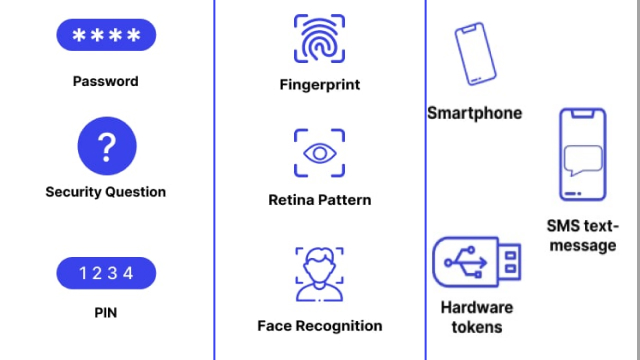
Other 2FA methods include biometric authentication, such as using your fingerprint or facial recognition, and email-based authentication, where a one-time code is sent to your email address. It’s important to choose a 2FA method that is convenient for you and provides a strong level of security for your accounts.
How Does SMS Two-Factor Authentication Work?
SMS (Short Message Service) two-factor authentication is a security feature that uses a user’s mobile phone number to verify their identity. When the user logs into an account, a verification code is sent to their mobile phone via SMS. The user then enters the code into the account login page to prove their identity and gain access.
SMS two-factor authentication is a popular method of adding an extra layer of security to online accounts. However, it is important to note that it is not foolproof and can be vulnerable to attacks such as SIM swapping. It is recommended to use additional methods of two-factor authentication, such as an authenticator app or hardware token, for increased security.
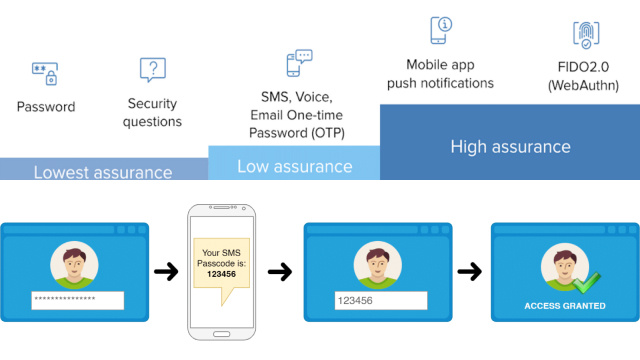
To use SMS two-factor authentication, the user must have a mobile phone number that can receive text messages. They will also need to enable the feature in their account settings and ensure that their phone number is up to date and correct.
How Does App-Based Two-Factor Authentication Work?
App-based two-factor authentication is a security process that adds an extra layer of protection to your online accounts. Instead of relying solely on a password, app-based 2FA requires you to enter a unique code generated by an authentication app.
To use app-based 2FA, you first need to download an authentication app, such as Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy. Once you’ve downloaded the app, you’ll need to set it up by linking it to your online accounts that support 2FA.
When you log in to your account, the authentication app generates a unique code that you need to enter along with your password. This code is only valid for a short period of time and changes regularly, providing an extra layer of security against hackers trying to gain access to your accounts.
App-based 2FA is considered to be one of the most secure forms of 2FA, as it is less vulnerable to phishing attacks and other forms of social engineering. It is important to note, however, that you should always use a strong, unique password in addition to 2FA to ensure the best possible security for your online accounts.
How Does Hardware Token Two-Factor Authentication Work?
Hardware token is a physical device that generates a one-time code, usually in the form of a six-digit number, to authenticate a user’s identity. It works by storing a secret key that is shared between the token and the authentication server.
When the user attempts to log in, they enter their username and password as usual, and then the hardware token generates a one-time code that the user must enter to complete the login process.
Hardware tokens are widely used in high-security environments such as government agencies, banks, and other financial institutions. They are considered one of the most secure methods of two-factor authentication since they are not vulnerable to hacking or phishing attacks.
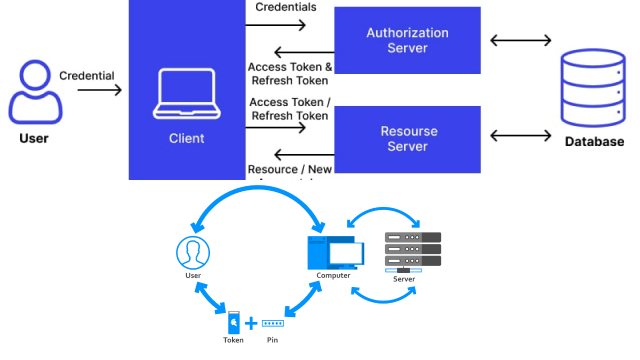
One of the main advantages of hardware token authentication is that the user does not need to have a phone or internet connection to generate the one-time code. Additionally, the codes are generated independently of the device being used to access the account, adding an extra layer of security.
However, hardware tokens can be expensive to implement and maintain, and users may find them inconvenient to carry around. As such, they are typically reserved for high-security applications or for users who require the highest level of security.
How Does Biometric Two-Factor Authentication Work?
Biometric two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security system that relies on a person’s unique physical characteristics to verify their identity. It works by using a biometric device, such as a fingerprint scanner or facial recognition technology, to confirm that the person trying to access a device or account is the authorized user.
When using biometric 2FA, the user’s biometric data is stored in a secure database and compared to the biometric data provided at login. If the two sets of data match, access is granted. Biometric 2FA is considered a strong security measure because it is difficult for an unauthorized person to replicate someone’s physical characteristics.
However, there are also potential risks with biometric 2FA. If the biometric data is stolen, it cannot be changed like a password can be. Additionally, some individuals may not have easily identifiable biometric markers, such as people with certain disabilities or medical conditions.
As with any security measure, it is important to weigh the benefits and risks of biometric 2FA and choose the best option for your needs.
How to Set Up Two-Factor Authentication and Keep Your Accounts Secure
Setting up two-factor authentication (2FA) is a simple yet effective way to keep your online accounts secure. Most websites and apps offer 2FA as an additional layer of security to the traditional username and password login.
To set up 2FA, you’ll need to choose the method you want to use for authentication, such as an app-based code generator, SMS verification, or a hardware token. Then, follow the prompts to activate 2FA on your account.
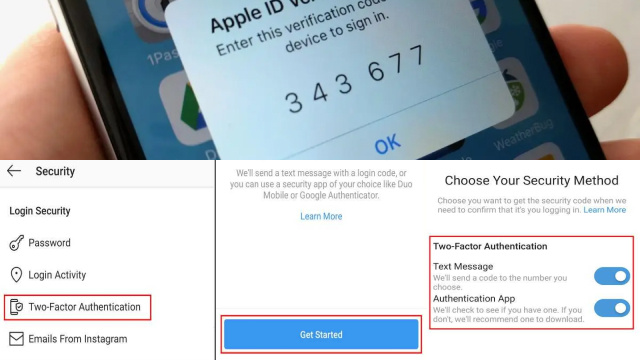
Once enabled, you’ll need to enter a code or approve a login request in addition to your username and password when accessing your account from a new device or location. This makes it much harder for hackers to gain access to your account, even if they have your password.
It’s important to note that 2FA is not foolproof, but it can greatly improve your account security. Remember to choose a strong and unique password and keep your 2FA device or method secure. By using 2FA, you’ll be taking an important step towards safeguarding your online accounts.