What is IP Spoofing?
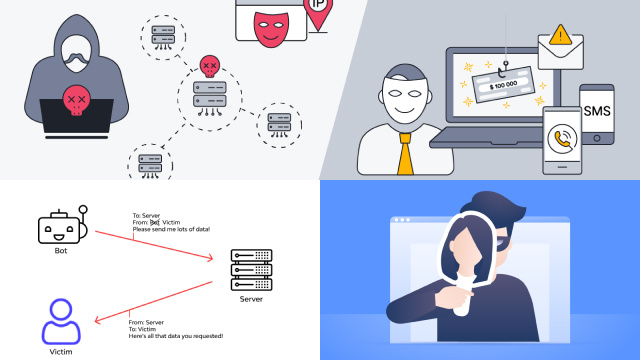
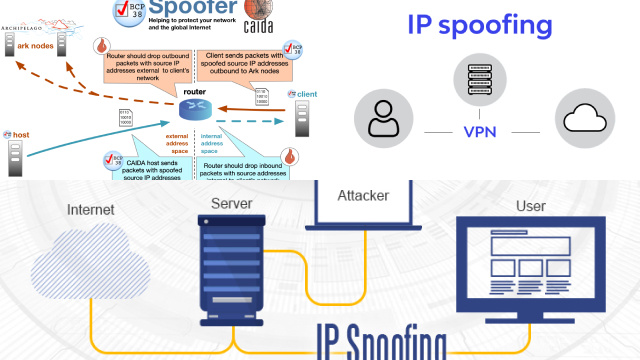
IP spoofing is a technique used by attackers to hide their identity while performing malicious activities over the internet. It involves forging the source IP address in the packets of a network connection, making it appear as though the traffic is coming from a different location than the attacker’s actual location.
The spoofed packets can be used to launch various types of attacks, including Denial of Service (DoS) attacks, phishing, and other network intrusions. Attackers can use this technique to bypass security measures that rely on IP address filtering or to impersonate a trusted source.
IP spoofing can be achieved through various means, including using special software tools or programming languages to modify packets. The potential consequences of IP spoofing can be severe, including data theft, service disruptions, and loss of reputation for affected organizations.
It’s important for individuals and organizations to take steps to prevent IP spoofing attacks, such as implementing firewalls, network segmentation, and using encryption to protect sensitive data.
How Does IP Spoofing Work?
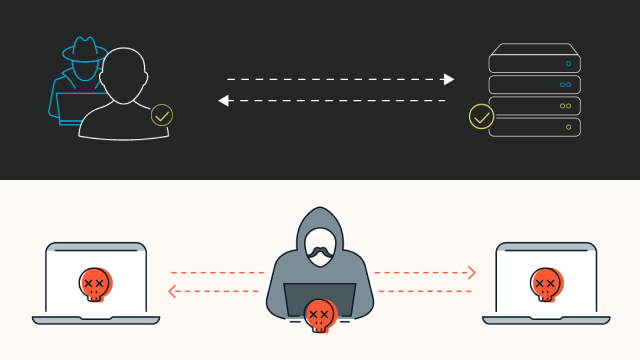
IP spoofing is a technique used by attackers to disguise their true identity and location by changing the source IP address of a packet. This technique can be used to launch various types of cyber attacks such as Denial of Service (DoS), Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), and Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks.
IP spoofing works by modifying the IP packet header to make it appear as if the packet was sent from a different IP address. The attacker creates a fake IP packet with a different source address, and sends it to the target system. When the target system receives the packet, it believes that it was sent from the fake IP address and responds accordingly. This allows the attacker to bypass security measures that rely on IP address filtering.
To prevent IP spoofing, network administrators can implement measures such as source address filtering, access control lists (ACLs), and ingress and egress filtering. These measures can help detect and block spoofed packets from entering the network, and protect against various types of cyber attacks.
Why Do Attackers Use IP Spoofing?
Attackers use IP spoofing for a variety of reasons, primarily to disguise their true identity and location. This technique allows them to bypass security measures and launch various types of cyber attacks such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), Man-in-the-Middle (MitM), and phishing attacks.
By spoofing their IP address, attackers can send packets to a target system without revealing their true location. This makes it difficult for the victim to identify the attacker or take legal action against them. In addition, IP spoofing can be used to evade security measures such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, allowing the attacker to gain unauthorized access to a network.
IP spoofing is also used in DDoS attacks, where a large number of spoofed packets are sent to overwhelm a target system’s resources. This can cause the system to crash or become unavailable, disrupting business operations and causing financial loss.
To protect against IP spoofing attacks, network administrators can implement measures such as source address filtering, access control lists (ACLs), and ingress and egress filtering. These measures can help detect and block spoofed packets from entering the network, and protect against various types of cyber attacks.
Impacts of IP Spoofing Attacks
IP spoofing attacks can have a significant impact on organizations and individuals, leading to financial loss, reputational damage, and even legal consequences. These attacks can be used to launch a variety of cyber attacks such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), Man-in-the-Middle (MitM), and phishing attacks.
In DDoS attacks, spoofed IP addresses can be used to overwhelm a target system’s resources, causing it to become unavailable or crash. This can disrupt business operations, cause financial loss, and damage the organization’s reputation. MitM attacks, on the other hand, can allow the attacker to intercept and modify communication between two parties, potentially stealing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, and other personal information.
In addition, IP spoofing attacks can be used to evade security measures such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, allowing the attacker to gain unauthorized access to a network. This can lead to the theft of sensitive data, such as intellectual property, trade secrets, and financial information.
To protect against IP spoofing attacks, network administrators can implement measures such as source address filtering, access control lists (ACLs), and ingress and egress filtering. These measures can help detect and block spoofed packets from entering the network, and protect against various types of cyber attacks.
How to Detect IP Spoofing
Detecting IP spoofing can be a challenging task, as attackers can use a variety of techniques to disguise their true identity and location. However, there are several methods that can be used to detect IP spoofing, including packet filtering, traffic analysis, and anomaly detection.
Packet filtering involves examining incoming packets and checking the source IP address against a list of trusted addresses. If the address is not on the list, the packet is dropped. This can help prevent spoofed packets from entering the network.
Traffic analysis involves monitoring network traffic and looking for patterns or anomalies that could indicate an IP spoofing attack. For example, a sudden increase in traffic from a particular IP address could indicate a DDoS attack.
Anomaly detection involves analyzing network traffic and looking for unusual behavior that could indicate an IP spoofing attack. For example, if a system suddenly starts sending a large number of packets with different source IP addresses, it could indicate an attempt to spoof the IP address.
To prevent IP spoofing attacks, network administrators can implement measures such as source address filtering, access control lists (ACLs), and ingress and egress filtering. These measures can help detect and block spoofed packets from entering the network, and protect against various types of cyber attacks.
How to Prevent IP Spoofing
Preventing IP spoofing attacks requires a combination of measures, including network configuration, software updates, and user education. Here are some methods that can be used to prevent IP spoofing:
- Source Address Verification: Implement source address verification to ensure that packets entering the network have a legitimate source address. This can be done through various mechanisms such as reverse path filtering, ingress and egress filtering, and access control lists (ACLs).
- Software Updates: Keep software and firmware up to date to prevent known vulnerabilities from being exploited by attackers.
- User Education: Educate users on the risks of IP spoofing and how to detect and prevent attacks. This can include training on safe browsing practices, email security, and the importance of using strong passwords.
- Network Segmentation: Segment the network to reduce the impact of a potential IP spoofing attack. This can be done through firewalls, VLANs, and other network segmentation techniques.
- Encryption: Use encryption technologies such as SSL/TLS to prevent attackers from intercepting and modifying network traffic.
By implementing these measures, organizations can reduce the risk of IP spoofing attacks and protect against various types of cyber attacks.
Tools for IP Spoofing Prevention
There are various tools and technologies available to prevent IP spoofing attacks. These tools work by detecting and blocking spoofed packets from entering the network. Some of the common tools used for IP spoofing prevention include:
- Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS): NIDS can detect and alert administrators about IP spoofing attacks by monitoring network traffic for unusual patterns or anomalies.
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP): BGP is a protocol used to exchange routing information between different autonomous systems (AS). It can be used to detect and prevent IP spoofing by verifying the legitimacy of the source IP address.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): ACLs can be used to filter incoming and outgoing traffic based on the source and destination IP addresses. This can help prevent spoofed packets from entering the network.
- Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF): RPF is a technique used to verify the legitimacy of the source IP address by checking the reverse path of the packet.
- Packet Filtering: Packet filtering involves dropping packets that have a source IP address that does not match the trusted addresses list.
By using these tools and technologies, organizations can prevent IP spoofing attacks and protect against various types of cyber attacks.
Best Practices for IP Spoofing Prevention
Implementing best practices for IP spoofing prevention is essential to protect organizations from cyber attacks. Here are some recommended best practices:
- Source Address Verification: Implement source address verification to ensure that packets entering the network have a legitimate source address.
- Network Segmentation: Segment the network to reduce the impact of a potential IP spoofing attack. This can be done through firewalls, VLANs, and other network segmentation techniques.
- Access Control: Restrict access to critical resources and limit user privileges to prevent attackers from gaining access to sensitive information.
- Encryption: Use encryption technologies such as SSL/TLS to prevent attackers from intercepting and modifying network traffic.
- User Education: Educate users on the risks of IP spoofing and how to detect and prevent attacks. This can include training on safe browsing practices, email security, and the importance of using strong passwords.
- Software Updates: Keep software and firmware up to date to prevent known vulnerabilities from being exploited by attackers.
By following these best practices, organizations can reduce the risk of IP spoofing attacks and protect against various types of cyber attacks.