Understanding VPN Port Forwarding: A Closer Look
VPN port forwarding is a powerful feature that allows you to establish direct connections to specific devices or services behind your VPN server. It enables you to access resources that are unreachable due to network configurations or firewalls.
In a typical VPN connection, all traffic is routed through the VPN server, which masks your IP address and encrypts your data for privacy and security. However, this can also result in some limitations, such as difficulty in accessing devices on your local network or using certain applications that require direct connections.
VPN port forwarding overcomes these limitations by selectively forwarding incoming connections to specific ports or IP addresses through the VPN tunnel, bypassing the usual routing through the VPN server. This allows you to access resources on your local network, use peer-to-peer applications, or host services like gaming servers or remote desktop connections.
Setting up VPN port forwarding involves configuring your VPN client and router settings, and it may require some technical knowledge. However, it can greatly enhance the functionality of your VPN connection and provide you with more control over your online activities.
In the next sections, we will delve deeper into how VPN port forwarding works and provide step-by-step instructions for setting it up, troubleshooting common issues, and optimizing its performance for a seamless experience.
How Does VPN Port Forwarding Work?
VPN port forwarding is a feature that allows you to establish direct connections to specific devices or services behind your VPN server. It works by selectively forwarding incoming connections to specific ports or IP addresses through the VPN tunnel, bypassing the usual routing through the VPN server.
When you initiate a connection to a device or service behind your VPN server, the incoming traffic is first encrypted and sent to the VPN server. The VPN server then forwards the traffic to the intended device or service using the port forwarding rules you have configured.
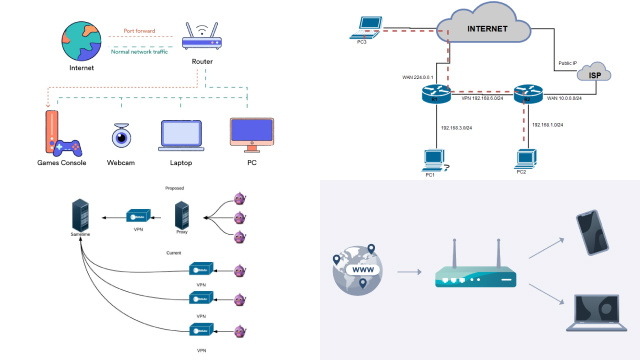
This process allows you to access resources on your local network or use applications that require direct connections, even though you are connected to a VPN. It enables you to bypass network configurations or firewalls that may block certain services or applications.
VPN port forwarding can be configured at both the client and router level. It involves setting up specific rules that define which incoming connections should be forwarded through the VPN tunnel. The exact steps for setting up VPN port forwarding may vary depending on the VPN client and router you are using.
In the next sections, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to set up VPN port forwarding, troubleshoot common issues, and optimize its performance for seamless connectivity.
Step-by-Step Guide: Setting Up VPN Port Forwarding
Setting up VPN port forwarding can seem daunting at first, but with the right instructions, it can be a straightforward process. Follow the step-by-step guide below to configure VPN port forwarding for your specific VPN client and router.
- Choose a VPN provider that supports port forwarding: Not all VPN providers offer port forwarding as a feature, so make sure to select one that supports it.
- Configure port forwarding on your router: Access your router’s settings and locate the port forwarding section. Create a new rule to forward incoming connections to the IP address of the device or service you want to access behind the VPN.
- Set up port forwarding on your VPN client: Some VPN clients have built-in port forwarding settings that allow you to specify which ports to forward. Configure the appropriate settings to match the port forwarding rule you set up on your router.
- Test your VPN port forwarding: Verify that the port forwarding is working properly by attempting to connect to the device or service from outside your network. If successful, you should be able to establish a direct connection.
- Troubleshoot common issues: If you encounter any issues, such as failed connections or dropped connections, double-check your settings, ensure that your router and VPN client are configured correctly, and consider consulting the VPN provider’s support resources.
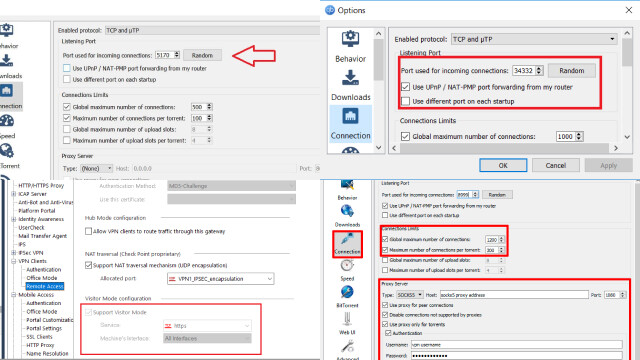
By following these steps, you can set up VPN port forwarding and unlock the ability to establish direct connections to devices or services behind your VPN server, opening up new possibilities for remote access and optimized performance.
Troubleshooting VPN Port Forwarding: Common Issues and Solutions
If you encounter issues with VPN port forwarding, don’t worry – there are common problems that can arise, but they can usually be resolved with some troubleshooting. Here are some common issues and solutions to help you troubleshoot VPN port forwarding:
- Port forwarding not working: Double-check your router and VPN client settings to ensure that they are correctly configured. Make sure the port forwarding rules match between the router and the VPN client settings.
- Firewall blocking incoming connections: Check if your firewall is blocking incoming connections to the forwarded ports. Adjust your firewall settings to allow incoming connections on the specified ports.
- IP address changes: If your device’s IP address changes, it may cause issues with VPN port forwarding. Make sure the IP address of the device you are forwarding to remains static or use a dynamic DNS service to keep it updated.
- Router firmware outdated: Outdated router firmware can cause port forwarding issues. Check for firmware updates and apply them if needed.
- VPN provider restrictions: Some VPN providers may have restrictions or limitations on port forwarding. Check with your VPN provider to ensure that they support port forwarding and that you are using the correct settings.
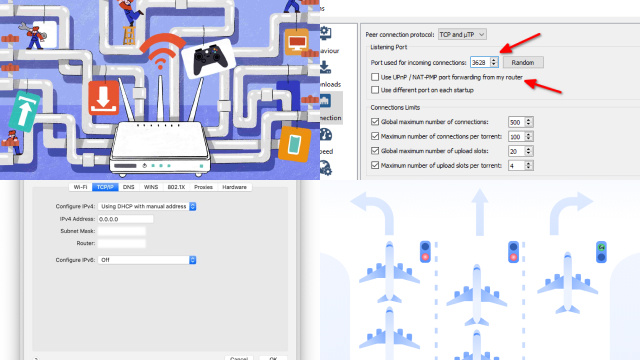
By addressing these common issues, you can troubleshoot VPN port forwarding and ensure that it is functioning properly for seamless remote access and optimized performance.
Advanced Tips for Optimizing VPN Port Forwarding
To optimize your VPN port forwarding for maximum performance and security, consider the following advanced tips:
- Choose a less commonly used port: Instead of using common ports like 80 or 443, consider using a less commonly used port for your port forwarding. This can help avoid potential conflicts or interference with other services or applications.
- Use a strong password: When setting up port forwarding, ensure that you use a strong and unique password for your router’s admin interface. This can help prevent unauthorized access to your router and protect your port forwarding settings.
- Enable UPnP: If your router supports Universal Plug and Play (UPnP), consider enabling it to automatically configure port forwarding for your VPN. However, exercise caution and ensure that your router’s UPnP feature is secure to prevent any potential security risks.
- Monitor for changes: Keep an eye on your VPN port forwarding settings and monitor for any changes. Sometimes, router updates or changes in network configurations can inadvertently affect port forwarding settings, so regular monitoring can help catch any discrepancies.
- Test regularly: Periodically test your VPN port forwarding to ensure that it is working as expected. Use online port checking tools or test your remote access to verify that your forwarded ports are open and accessible.
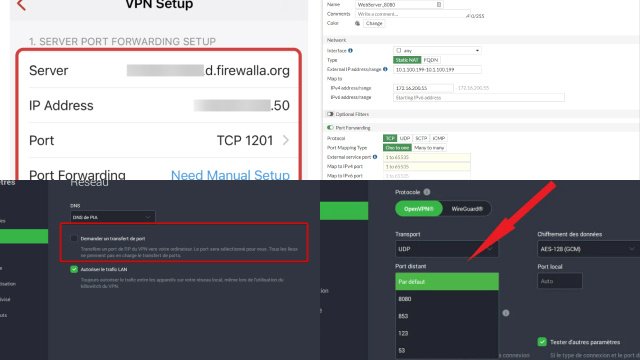
By implementing these advanced tips, you can optimize your VPN port forwarding for enhanced performance, security, and reliability, allowing you to make the most out of your VPN connection.
Use Cases and Scenarios: When to Implement VPN Port Forwarding for Enhanced Connectivity
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are essential for securing online activities, but VPN port forwarding becomes crucial in specific scenarios, enhancing connectivity:
- Gaming: Gamers benefit from VPN port forwarding as it reduces latency by allowing direct game server connections. This ensures a smoother gaming experience.
- P2P File Sharing: For torrenting and P2P sharing, port forwarding enables faster download and upload speeds by permitting incoming connections.
- Remote Access: VPN port forwarding facilitates remote access to home or office networks. This is invaluable for remote work, accessing files, or managing IoT devices.
- VoIP Calls: Voice and video calls over VPNs can suffer from poor quality. Port forwarding optimizes VoIP by streamlining data flow.
- Media Streaming: If you’re traveling and want to access region-locked content on streaming platforms, port forwarding can help you bypass restrictions.
- Security Cameras: For remote monitoring of security cameras, VPN port forwarding ensures uninterrupted access to live feeds.
In these use cases, VPN port forwarding enhances connectivity by streamlining data flow and bypassing potential bottlenecks, improving the overall online experience.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of VPN Port Forwarding
VPN port forwarding can be a powerful tool to enhance your online privacy, security, and accessibility. By understanding how VPN port forwarding works and following the step-by-step guide for setting it up, you can unlock new possibilities for remote access, online gaming, file sharing, and more.
However, it’s important to be aware of common issues and troubleshooting solutions to ensure smooth operation. By troubleshooting and optimizing your VPN port forwarding settings, you can overcome potential challenges and enjoy a seamless experience.
With advanced tips such as choosing less commonly used ports, using strong passwords, enabling UPnP cautiously, monitoring for changes, and regularly testing your port forwarding, you can further optimize your setup for maximum performance and security.
In conclusion, harnessing the power of VPN port forwarding can elevate your online experience to a new level, providing you with added control, flexibility, and security in your online activities.