Check Point experts have prepared the Global Threat Index report dedicated to the most active threats of August 2019. Analysts note the activity of the Echobot botnet, as well as the “return to life” of the Emotet botnet.
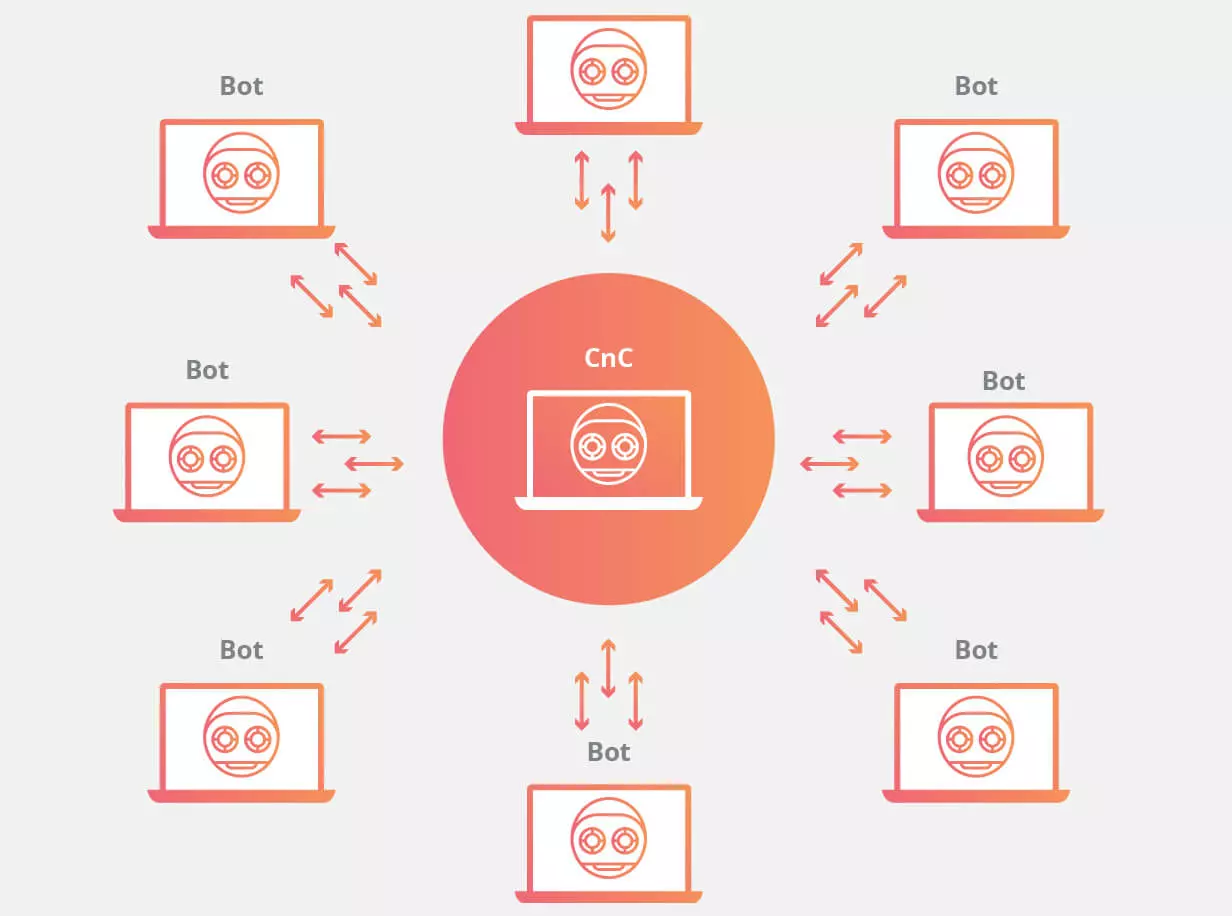
In the report, the research group warns of a new version of the botnet Mirai – Echobot, which began large-scale attacks on smart devices. Echobot appeared in May 2019, and has since “learned” to exploit more than 50 different vulnerabilities. Malvar is particularly active in exploiting the problems of Command Injection Over HTTP. Echobot attacks have already affected 34% of organizations around the world.
– comments Vasily Diaghilev, head of Check Point Software Technologies in Russia and the CIS.
As the researchers assumed, in August the infrastructure of another botnet, Emotet, was reactivated. The fact is that a couple of months ago, in June 2019, the number of malicious campaigns Emotet sharply decreased. The Check Point team then suggested that the botnet infrastructure could be shut down for maintenance and updates. We have already noted that the “vacation” of Emotet operators is not an unusual case. Botnets often take breaks in operation, updating the infrastructure, or while their operators are resting. For example, the famous Dridex botnet was shut down every year from mid-December to mid-January, during the winter holidays.
As a result, the top most active malawari in August 2019 looks as follows.
Emerging Cybersecurity Threats in 2025: Staying Ahead of Evolving Dangers
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, staying ahead of emerging threats is essential to protect sensitive data and digital assets. As we move into 2023, new challenges and vulnerabilities are emerging. Here are some of the cybersecurity threats to watch out for and proactive measures to safeguard your digital presence:
- Ransomware Evolution: Ransomware attacks continue to adapt, with threats like double extortion and triple extortion, where attackers not only encrypt data but also threaten to release it or sell it. Employing robust backup solutions and educating users about phishing risks are essential.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting supply chains to compromise trusted software and services. Companies should conduct thorough security assessments of their vendors and partners.
- AI-Powered Threats: Malicious use of artificial intelligence (AI) is on the rise, enabling more sophisticated attacks. AI-driven security solutions are necessary to counter these threats.
- Deepfake and Synthetic Media: The spread of deepfake videos and synthetic content poses reputational and security risks. Organizations should implement policies for verifying media content and enhancing authentication processes.
- Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: The discovery and exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities can lead to critical breaches. Timely patch management and intrusion detection systems are vital for protection.
- IoT and Edge Devices: With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) and edge devices, new entry points for cyberattacks are created. Network segmentation and device management are essential for security.
- Cloud Security: As more data moves to the cloud, securing cloud environments becomes paramount. Implementing strong access controls, encryption, and regular audits is crucial.
- Quantum Computing Threats: While still in the early stages, quantum computing poses a potential threat to current encryption methods. Preparing for quantum-safe encryption is a long-term security strategy.
- Regulatory Compliance: Evolving data privacy regulations and compliance requirements demand ongoing attention and adherence to avoid legal consequences.
- User Training and Awareness: Cybersecurity education for users remains a frontline defense. Regular training on recognizing phishing attempts and safe online practices is essential.
In a rapidly changing digital landscape, proactive cybersecurity strategies are key to staying ahead of emerging threats. Continuously monitoring and adapting to new challenges, implementing robust security measures, and fostering a culture of cyber-awareness are critical to protecting against evolving dangers in 2023 and beyond.
The most active miner in the world in August 2019:
- XMRig – open source software first discovered in May 2017. Used for mining of Monero cryptocurrency
- Jsecoin is a JavaScript miner that can run the miner directly in your browser in exchange for advertising, in-game currency and other incentives.
- Dorkbot is an IRC-based worm designed to run code remotely by its operator and to download additional malware to an infected system.
Most active mobile threats in August 2019:
- Lotoor is a program that exploits vulnerabilities in the Android operating system to gain privileged root access to hacked mobile devices
- AndroidBauts is an advertising malware that steals IMEI, IMSI, GPS data and other device information and allows you to install third-party applications on infected mobile devices.
- Triada is a modular backdoor that provides superuser privileges for downloaded malware and helps to integrate them into system processes. Triada has also been seen to be swapping URLs that are downloaded from the browser.