While it might seem obvious to some, many might wonder: why even bother making a list of the most important cyber security threats? Experts certainly do not need this list of computer security threats to know how to do their job and to get ready for next year’s trends. The truth is that people are the main cyber threat and that articles like this one are aimed at educating them and making them aware of this very fact.
A report1 has found that 99% of cyberattacks wouldn’t be possible without the intervention and/or unknowing participation of humans. People are the main computer security vulnerability, the weak link. There are many examples in the list below, but a good example of vulnerability caused by humans is software or hardware not being properly updated. Humans are a source of unpredictability and can fall victim to social hacking or compromise sensitive data by inappropriately using their devices or applications. Education is therefore extremely important to making people realize that it is impossible to build a perfectly safe computer system if users to not follow the safety guidelines and take time to learn to safely use the tools at their disposal.
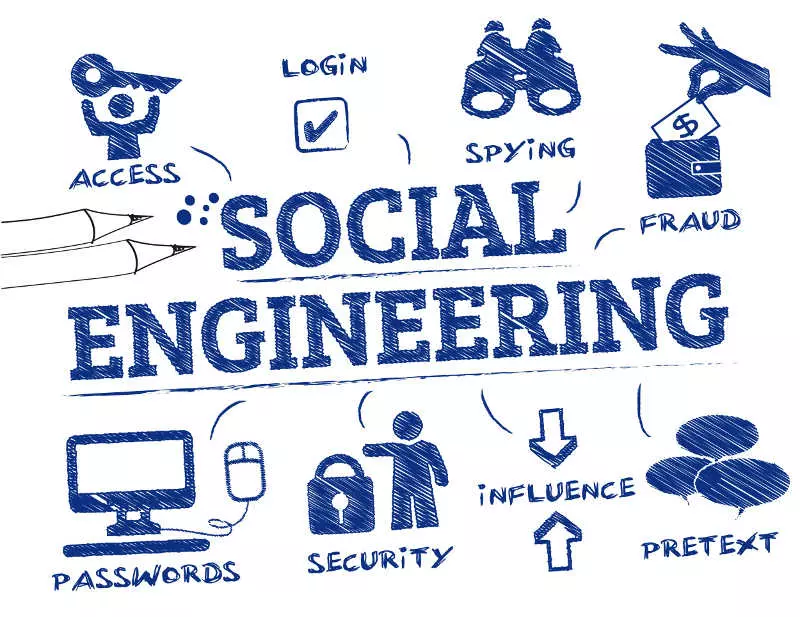
Cyber Security Threat 1: Social Engineering
Psychologically manipulating people to obtain sensitive information has existed long before the rise of computers. However, this certainly reached a new scale and frequency with the internet. Even with the best spam filters, we have all unfortunately gotten used to receiving suspicious emails, texts or even voicemails. These are called phishing attacks, one of the most common forms of social engineering. Phishers will send you an email (or text or voicemail), make it appear as if it came from a legitimate source (your bank, an online account of yours, etc.) and trick you into sending them confidential information. As a result the user may loose his money or strangers will get saccess to his personal data.
While most of us can easily deflect “broad sweep” phishing attacks (the famous “Nigerian Prince”), targeted social engineering attacks can be quite sophisticated and hard to detect. As always, being educated and using your critical thinking is key, although not always easy in practice, in today’s fast-paced world where we are used to making thousands of quick decisions and clicks.
Cyber Security Threat 2: Ransomware
Everyone was made aware of ransomware over the past few years due to several highly publicized cases. It is a type of malware that uses a Trojan to acquire sensitive information (webcam feed, passwords, etc.) to lock your computer system and then ask you for a ransom. The brilliant part about it is that hackers not only ask for a “reasonable” amount of money but also do unlock your system afterwards, making it all the more likely that you will pay to make it go away. Attackers have you pay using some sort of cryptocurrency, making it very difficult to trace them.
Cyber Security Threat 3: IoT threats
The Internet of Things (IoT) was once regarded as the next revolution. While it never quite happened that way, the market has been growing year after year. The numbers associated with smart speakers (think Alexa, Google Home, Facebook portal, etc.) alone makes one’s head turn: a study2 suggests that, in the US alone, 164 million units will be sold in 2019, totaling 250 million of units installed.
IoT devices bring a lot of useful and convenient features by being connected to the internet and to one another. But that convenience comes at a cost: vulnerability. Because they are connected to the internet, they can be exploited by hackers as a point of entry to your network. Furthermore, a lot of these devices (especially the cheaper ones) were not designed to have any security updates (or patching). This is why digital security risks associated with the IoT are dubbed to become the biggest cyber threat in the coming years.
And while industry actors and security experts are developing universal standards, there will always be the problem of all the IoT devices that have already been sold.
Cyber Security Threat 4: Mobile threats
There has been a lot of news in 2018 and 2019 regarding mobile apps that made it to Google’s Play Store or Apple’s App Store despite containing malicious code. The two main threats here concern privacy (attackers target your data to resell it) and crypto-mining malware (also known as cyptojacking). This is all the more concerning as a survey by Cisco estimates that 95% of business already allows employee-owned personal devices (BYOD) in one way or another3.
Cyber Security Threat 5: AI/ML attacks
There are already plenty of worrying and persistent digital security risks, but one of the most distressing internet security threats is the rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning-driven attacks. More and more companies should start seeing botnet attacks powered by AI/ML.
Fortunately, most hackers don’t yet have the knowledge or the means to leverage such powerful tools, with the exception of nation-sponsored syndicates. More good news is that, while AI/ML can be used for evil, they also will help make our systems much more secure.
Cyber Security Threat 6: Data Rights compliance
This is not new, but with last year’s major regulations, particularly in Europe (the GDPR) and California (the CCPA), data compliance makes for a fast-changing environment open to vulnerabilities. Stricter data protection legislation is always good news for the users and badly needed in our day and age. However, as internet services implement these and try to adapt in time, they might open the door to new vulnerabilities. It is also important to say that meeting data compliance standards is never a guarantee of proper data protection.
And the interconnected nature of the internet and the economy means that such changes have a very wide reach. Hackers are certainly looking at exploiting GDPR and CCPA regulatory procedures to their advantage. As with any major change, it is important not to rush the process and make sure to keep security at the heart of any privacy-driven solution.
Cyber Security Threat 7: Cloud vulnerabilities
The cloud is one of the best examples of third-party vulnerability. Individuals and companies alike rely more and more heavily on the cloud, which makes it all the more prone to a major breach or Denial of Service (Dos) attack. The most important thing to remember, especially in a business setting, is that it is not because you rely on a third-party cloud provider that you are not responsible for the integrity and confidentiality of the data. While it can be hard to choose a cloud provider, it is imperative to take the time to check their security track-record.
Conclusion
There are many more digital security risks out there – too many to list – but these represent the seven main trends regarding cyber threats in 2020. The online environment is always evolving and it is always possible for new, unforeseen security vulnerabilities to emerge.
Educating yourself is the first step to protecting you from such risks.
Because, remember, another way that “people are the main cyber security threat” is true is that, behind every attack, there is a malicious party, someone trying to gain access to your data or exploit a vulnerability to his advantage.