In an online world, “cache” and “cookies” are two sides of a coin. Cookies help a website know what you have seen last and check if your preferences have changed as well. Cache speeds up the loading times by sending the finer web page details directly to you. Although cache and cookies seem similar, each of them has a different function of making your online experience easier or more personalized. Let’s find out more.
What is Cache?
The cache is hidden from the user. In most cases. It is a buffer between the browser and the internet, where pages visited by the user are stored. When you open any websites, cards, images, videos, their copies remain in the browser’s memory. This happens even if you do not download content but simply view it. These copies are called cache. It is needed to reduce the number of requests to websites. For example, after some time, you decide to view a page again that you opened before. The cache will instantly load it from the hard drive.
Do I Need to Clear Cache?
Cleaning your cache will help to improve the performance of your browser and it will be easier for you to see the most updated version of websites, but it won’t always make a difference.
Clear your cache if you visit many different sites or if you share your device with others; otherwise, you don’t have to do it.
A cookie is a small piece of data stored on a user’s computer. It contains information related to the user, including their preferences and actions on a specific website: authentication data (username and password), individual settings, visited pages, performed actions, items in the shopping cart, date and time of visits, etc. When a user revisits a website, the browser sends a cookie to the server to inform the site about the user’s previous activities. Cookies have a certain lifespan, after which they are deleted.
>> How to Enable or Disable Cookies in Chrome, IE, Firefox, Edge, and Safari

Cookies help improve the user experience, making online work more comfortable and faster. Let’s provide examples of use:
- User authentication: Thanks to cookies, users do not have to enter their login and password again whenever they visit a site.
- Online shopping: Cookies allow remembering selected items, so they remain in the cart even if the site/application is closed.
- Personal preferences and user settings: Saving this data helps avoid reconfiguring the region, language, design style, etc., with each visit.
Following the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), websites must inform users about the use of cookies, which they do using pop-up windows. It is possible to refuse to use cookies (if such an option is provided), and according to GDPR rules, access to the service will not be prohibited or restricted. However, it is essential to remember that in this case, using, for example, an online store will become inconvenient.
Do I need to Clear Cookies?
Clearing cookies helps protect your privacy but you’ll need to re-enter logins and preferences on websites.
Browser Cache vs Cookies: Comparison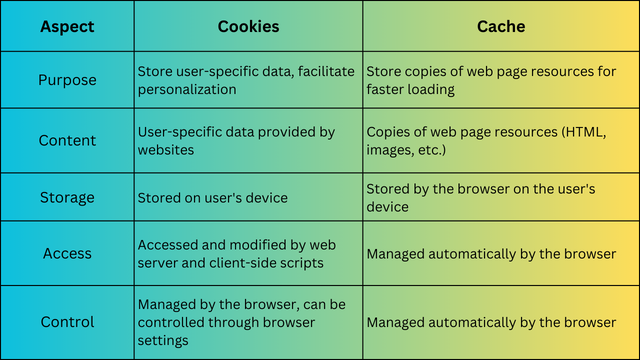
So, in summary:
Cache: A storage area on the hard disk used by browsers to store web objects temporarily, helping to load websites faster by saving frequently accessed resources.
Cookies: Small text files stored on the client’s computer (and sometimes on the server side) containing information useful for websites, such as login credentials, preferences, and other data.