Common Reasons Why Windows Won’t Boot
Windows not booting can be a frustrating issue for users. Here are some common reasons why your Windows may not be booting up:
- Hardware issues: If you recently installed new hardware or made changes to your computer, such as replacing the motherboard or RAM, it could cause Windows not to boot up properly.
- Corrupted boot files: Boot files are essential for the operating system to start up correctly. If they are corrupted or damaged, it can cause Windows not to boot.
- Driver issues: Incompatible or outdated drivers can cause Windows not to boot up.
- Virus or malware infections: Malware or virus infections can also prevent Windows from booting up.
- Power supply problems: If your power supply is not working correctly, it can cause your computer to fail to boot up.
Identifying the underlying cause of your Windows booting issue is essential to fix the problem. Once you have identified the problem, you can proceed with troubleshooting and fixing it.
How to Troubleshoot Windows Booting Issues
If your Windows won’t boot up, there are several steps you can take to troubleshoot the issue.
- First, check your hardware: Make sure all cables and power connections are securely plugged in.
- Try booting in Safe Mode: This will load a basic version of Windows and help you identify if the issue is software-related.
- Check for any recent changes: Did you recently install new hardware or software? This could be causing the issue.
- Use the Command Prompt: Use the Command Prompt to run a series of diagnostic tests to identify and fix issues.
- Run System Restore: System Restore can help you restore your system to an earlier point in time, before the issue began.
- Use Startup Repair: Use the Startup Repair tool to scan and repair your system’s boot files.
- Reinstall Windows: As a last resort, you can reinstall Windows to fix booting issues.
By following these steps, you can troubleshoot and fix common Windows booting issues.
Use Safe Mode to Fix Windows Boot Problems
Safe Mode is a diagnostic startup mode in Windows that can help you troubleshoot and fix boot problems. To enter Safe Mode, restart your computer and continuously press the F8 key until the Advanced Boot Options menu appears. From there, select Safe Mode.
Once you’re in Safe Mode, you can identify and fix the problem that is causing Windows not to boot. You can try uninstalling any recently installed software or hardware, running a virus scan, or using the System Restore feature to restore your system to an earlier point in time.
Safe Mode loads only essential drivers and services, so if Windows starts up correctly in Safe Mode, it indicates that the issue is likely related to software or drivers. Using Safe Mode to troubleshoot and fix boot problems can save you time and money by avoiding the need for professional help or costly repairs.
Repair Windows Boot Files Using the Command Prompt
If Windows won’t boot up properly, you can use the Command Prompt to repair boot files. Here’s how:
- Boot your computer from a Windows installation disk or USB drive.
- Select your language preferences, then click on “Repair your computer.”
- Choose “Troubleshoot” > “Advanced options” > “Command Prompt.”
- Type the following commands in the Command Prompt, pressing Enter after each one:
bootrec /fixmbr bootrec /fixboot bootrec /scanos bootrec /rebuildbcd
These commands will repair the Master Boot Record (MBR), the boot sector, and rebuild the Boot Configuration Data (BCD) store.
Recovering Your System Using System Restore
If you’ve encountered a problem with Windows booting up, you may be able to use System Restore to recover your system to a previous working state. Here’s how to use it:
- Boot your computer from a Windows installation disk or USB drive.
- Select your language preferences, then click on “Repair your computer.”
- Choose “Troubleshoot” > “Advanced options” > “System Restore.”
- Select the restore point you want to use and follow the prompts to restore your system.
System Restore will revert your computer’s settings to a previous state, undoing any changes that might have caused your Windows booting problems.
Note that System Restore won’t fix all booting issues, and you must have had a restore point created before the problem occurred. If System Restore doesn’t work, you may need to try other troubleshooting methods or seek professional help.
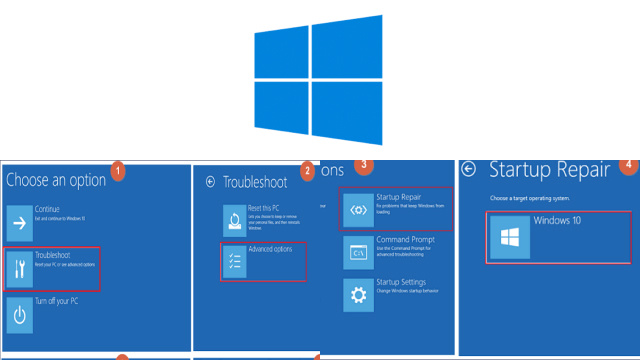
Fixing Windows Boot Problems with Startup Repair
If you’re experiencing Windows boot problems, one troubleshooting method you can try is using the Startup Repair tool. Here’s how to use it:
- Boot your computer from a Windows installation disk or USB drive.
- Select your language preferences, then click on “Repair your computer.”
- Choose “Troubleshoot” > “Advanced options” > “Startup Repair.”
- The tool will attempt to diagnose and repair any issues preventing your Windows operating system from starting up.
If the tool is unable to fix the problem, it will provide you with a report on what it found and what actions it took. In some cases, you may need to run the tool multiple times for it to work.
Note that Startup Repair won’t fix all booting issues, and you may need to try other troubleshooting methods or seek professional help if the problem persists.
Reinstalling Windows to Fix Boot Issues
If you’ve tried other troubleshooting methods and still can’t get Windows to boot, reinstalling the operating system may be your best option. This will erase all data on your computer, so be sure to backup any important files before proceeding.
To reinstall Windows, you’ll need a bootable Windows installation disk or USB drive. Here’s how to do it:
- Insert the installation disk or USB drive and restart your computer.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to boot from the disk or drive and begin the installation process.
- When prompted, choose the option to “Custom install” and select the partition where you want to install Windows.
- Follow the remaining prompts to complete the installation process.
After the installation is complete, you’ll need to reinstall any programs and restore any data from your backup. This may be a time-consuming process, but it can be an effective solution for booting issues that other methods couldn’t fix.
When All Else Fails: Seeking Professional Help for Windows Boot Problems
If you’ve exhausted all the troubleshooting methods for Windows boot problems and are still unable to resolve the issue, it may be time to seek professional help. There are several options available:
- Contact the manufacturer of your computer or your operating system provider for support. They may have specific tools or resources to help diagnose and fix booting issues.
- Take your computer to a local repair shop or a professional technician who specializes in computer repairs. They may have more advanced tools and expertise to identify and fix the problem.
- Join online communities or forums related to your operating system or computer brand. You can ask for advice or recommendations from other users who may have encountered similar issues.
Remember to backup your important data before seeking professional help, as any repair or reinstallation of your operating system may result in data loss.