Understanding Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering attacks are a type of cyberattack that exploits human behavior to gain access to sensitive information or computer systems. Rather than relying on technical vulnerabilities, social engineering attacks exploit the trust and naivety of individuals through techniques such as phishing, pretexting, and baiting.

Phishing involves sending fraudulent emails or messages that appear to come from legitimate sources, such as banks or government agencies, and tricking users into disclosing sensitive information such as passwords or financial data. Pretexting involves creating a false sense of trust by impersonating someone else, such as a tech support representative or a co-worker, in order to gain access to confidential information. Baiting involves leaving a tempting item, such as a USB drive, in a public place in the hopes that someone will pick it up and plug it into their computer, unwittingly giving the attacker access to their system.
Understanding the tactics used in social engineering attacks is crucial in order to protect against them. By staying vigilant and skeptical of unsolicited messages or requests, individuals can avoid falling victim to these types of attacks.
Common Techniques Used in Social Engineering
Social engineering is a common tactic used by cyber criminals to manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information or granting access to secure systems. There are several techniques that social engineers use to exploit human behavior, including pretexting, phishing, baiting, and tailgating.
Pretexting involves using a fabricated scenario to gain the trust of the victim, such as impersonating a colleague or authority figure. Phishing involves creating fraudulent emails or websites that appear to be legitimate, with the aim of tricking the victim into providing sensitive information. Baiting involves leaving physical media, such as a USB drive, in a public place in the hope that someone will plug it into their computer, allowing the attacker to access the system. Tailgating involves following an authorized person into a restricted area without permission.
Social engineering attacks can be devastating, as they often go undetected for long periods of time. It’s essential to remain vigilant and be cautious of unsolicited requests for information or access. By understanding common social engineering techniques, individuals can better protect themselves and their sensitive information from cyber attacks.
The Human Factor in Social Engineering
The human factor is a critical component in social engineering attacks. Cyber criminals exploit human behavior to manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information or granting access to secure systems. Unlike traditional cyber attacks, social engineering attacks focus on manipulating the human element rather than technical vulnerabilities.
Social engineering tactics such as pretexting, phishing, baiting, and tailgating rely on the trust and naivety of individuals. Social engineers will often do extensive research on their targets, gathering information from social media and other online sources to tailor their attacks and increase their chances of success.

Despite advances in technology and security measures, the human factor remains the weakest link in cybersecurity. Training and education can play a critical role in preventing social engineering attacks. By raising awareness and providing employees with the tools and knowledge to recognize and respond to social engineering attacks, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to these types of attacks.
In conclusion, the human factor is a crucial component in social engineering attacks, and organizations must remain vigilant in their efforts to educate employees and protect against these increasingly sophisticated attacks.
Social Engineering in the Digital Age
In the digital age, social engineering attacks have become increasingly prevalent, with cyber criminals using a range of tactics to exploit human behavior and gain access to sensitive information. The rise of social media and other online platforms has made it easier than ever for attackers to gather information on their targets, tailoring their attacks to increase their chances of success.
Common social engineering tactics used in the digital age include phishing, where attackers send fraudulent emails or messages designed to trick individuals into providing sensitive information, and pretexting, where attackers impersonate someone else, such as a tech support representative, to gain access to confidential information.
As technology continues to advance, so too will social engineering tactics, making it crucial for individuals and organizations to stay vigilant and aware of the risks. Education and training can play a key role in preventing social engineering attacks, helping individuals to recognize and respond to these increasingly sophisticated attacks. By taking proactive steps to protect against social engineering, individuals and organizations can reduce their risk of falling victim to these types of attacks.
Tips for Recognizing Social Engineering Attempts
Recognizing social engineering attempts is essential to protect yourself and your sensitive information from cybercriminals. Here are some tips to help you spot potential social engineering attacks:
- Be wary of unsolicited requests for information or access.
- Be suspicious of requests that create a sense of urgency or fear.
- Watch for inconsistencies or discrepancies in messages or communication.
- Be cautious of messages or communication that seem too good to be true.
- Always verify the identity of someone requesting sensitive information or access.
- Be wary of requests that ask you to bypass security protocols or procedures.
- Keep your personal information private and secure, and limit the information you share online.
- Stay informed about the latest social engineering tactics and remain vigilant in your efforts to protect against them.

By following these tips and staying alert to the signs of social engineering attempts, you can reduce your risk of falling victim to these types of attacks and help protect your sensitive information.
Best Practices for Preventing Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering attacks can have devastating consequences for individuals and organizations, but there are steps you can take to prevent them. Here are some best practices for preventing social engineering attacks:
- Educate yourself and your employees about social engineering tactics and how to recognize them.
- Establish strong security protocols and procedures, and ensure that they are followed consistently.
- Use multi-factor authentication to secure sensitive accounts and systems.
- Regularly update and patch software and systems to address security vulnerabilities.
- Limit the amount of personal information shared online and on social media.
- Conduct background checks and verification of vendors and contractors who have access to sensitive information or systems.
- Encourage a culture of security awareness and responsibility within your organization.
- Regularly review and evaluate your security practices and procedures, and adjust them as necessary.
By following these best practices, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to social engineering attacks and protect yourself and your organization against cyber threats.
Creating a Strong Security Culture in Your Organization
Creating a strong security culture in your organization is essential to protecting against cyber threats and keeping sensitive information secure. Here are some tips to help establish a strong security culture in your organization:
- Start at the top. Leaders must lead by example and demonstrate a commitment to security.
- Educate employees on the importance of security and the potential risks associated with cyber threats.
- Develop clear policies and procedures for security practices, and make sure they are communicated effectively to all employees.
- Use security technologies, such as firewalls and antivirus software, to protect against cyber threats.
- Encourage employees to report security incidents and provide a process for them to do so.
- Regularly assess security practices and adjust as necessary.
- Use incentives and rewards to encourage good security practices.
- Hold regular training sessions and provide ongoing education on security best practices.
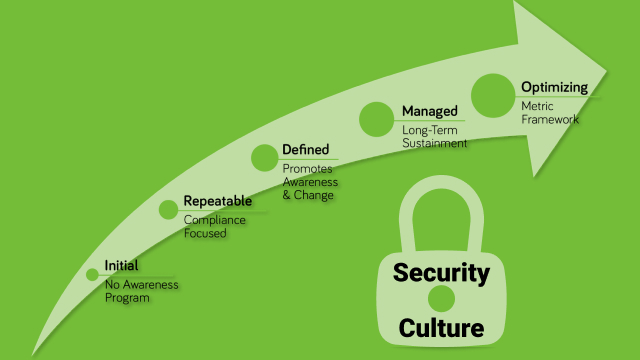
By creating a strong security culture in your organization, you can help protect against cyber threats and keep sensitive information secure. It is important to make security a priority and establish a proactive approach to protecting against cyber threats.
The Importance of Regular Security Training and Awareness Programs
Regular security training and awareness programs are critical for organizations to keep their employees informed about the latest cyber threats and how to protect against them. These programs help employees understand the importance of security and the role they play in maintaining it.
It is essential to provide ongoing training to ensure that employees stay up-to-date on the latest security threats and how to recognize and avoid them. Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics, so it is crucial to provide employees with the knowledge and skills they need to identify and respond to new threats.
Regular security training and awareness programs can also help reduce the risk of security incidents and data breaches, which can be costly and damaging to an organization’s reputation. By investing in regular security training and awareness programs, organizations can help protect their sensitive information and assets, and build a culture of security awareness and responsibility.
